First post of a series
As we begin this series exploring the transformative impact of Generative AI on book publishing, it’s clear that we are witnessing one of the most significant disruptions the industry has seen in decades.
In this introductory post, we'll first focus on the unique aspects of book publishing, especially those that may be less familiar to many readers, such as the different subcategories within the industry, and the key business developments of the past 15 years.
The main categories of book publishing
Consumer publishing (also known as Trade publishing): this category includes fiction and non-fiction aimed at general readers, and children’s books. These books are primarily sold through bookstores and online retailers. (Note that in some industry reports, children's books are treated as a separate category).
Educational publishing: includes textbooks and educational resources used in schools, colleges, and other learning institutions.
Academic publishing: this sector focuses on scholarly works like research papers, journals, monographs, and publications from university presses, including books for university students.
Professional publishing: this category targets professionals in specific industries, with publications such as legal texts, technical manuals, and business books.
Globally, book publishing is a substantial industry. Leading research firm Ibis World estimated its worth at $147.4 billion in 2023, while PWC valued it at $129 billion for the same year. To put this into perspective, the global video streaming (SVoD) market, including platforms like Netflix and Amazon Prime, was valued at $108.5 billion in 2024 (Statista).
In this post, we’ll focus on consumer book publishing, which accounts for the largest share of readers and revenue. According to the Association of American Publishers (AAP Data), consumer books make up 63% of the total publishing revenue in the US, while the Federation of European Publishers reports a 65.6% share in Europe (FEP Data).
The unique resilience of trade book publishing
Unlike newspapers and magazines, which have seen readership and advertising revenues plummet in the digital era, consumer books have maintained their popularity. While digital products like e-books and audiobooks are important, they haven’t annihilated print as digital downloads and streaming replaced CDs in music or DVDs in home entertainment. Instead, these digital formats have complemented print books, opening up new profitable avenues for publishers rather than becoming existential threats.
Moreover, the core business model of trade book publishing has remained remarkably stable compared to other publishing sectors:
Fifty years ago, newspapers primarily earned revenue by selling readership to advertisers. Today, after a tough transition, quality newspapers generate the most income by selling (digital) content to readers via subscriptions.
In contrast, consumer book publishers’ main source of revenue—selling content directly to readers—remains largely unchanged. Fifty years ago, this revenue came solely from physical books; today, it includes both physical and digital formats.
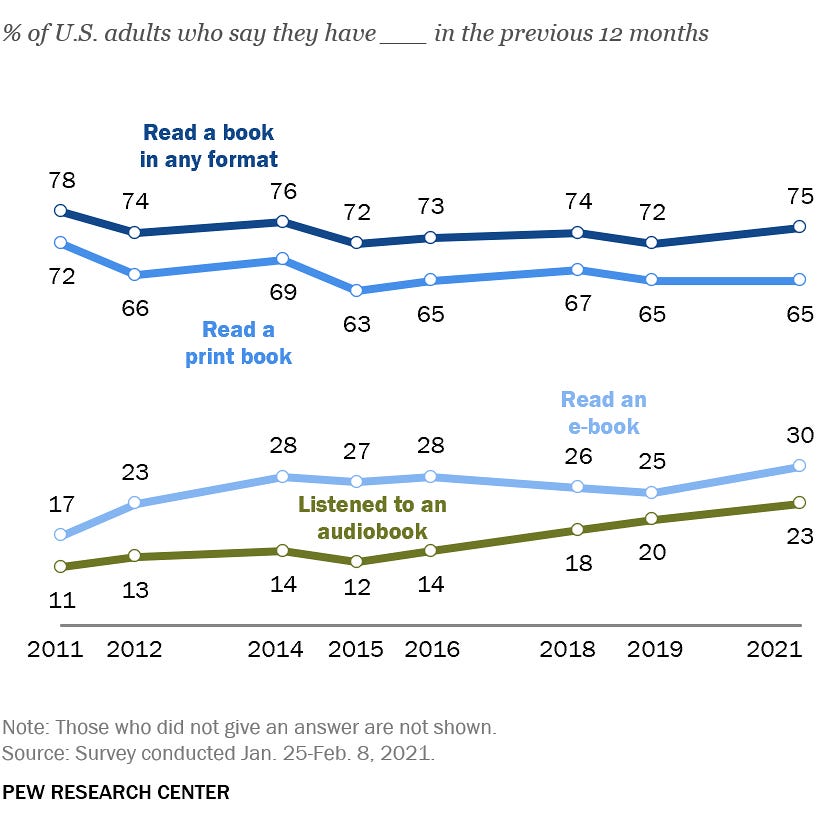
In summary, print books remain the first revenue source for trade publishers in most countries, as readers still cherish physical books and attach emotional value to them. This is further supported by book readership statistics from various nations, as illustrated by the PEW survey below for the US.
Incremental innovation in the digital era
This is not to say that trade book publishing hasn’t innovated or remained untouched by the digital revolution:
E-commerce: Publishers had to adapt to e-commerce earlier than most other industries, largely due to Amazon's rise after launching as an online bookseller in 1994.
E-books: The Kindle’s debut in 2007, along with the growth of self-publishing, made e-books a prominent (and profitable) market segment.
Audiobooks: Digital audiobooks have grown significantly in popularity over the past five years, and continue to rise.
Social Media: Platforms like TikTok have had a significant influence, particularly through #BookTok, which has attracted millions of posts and billions of views since 2020. This phenomenon has encouraged a new generation of young readers to embrace books, much like the Harry Potter generation did years ago.
However, these innovations were incremental, unfolding gradually over several years. Amazon, for example, became the leading bookseller in the US nearly a decade after its establishment, while its dominance in other countries took even longer. Unlike other creative industries, trade book publishing wasn’t forced to reinvent itself overnight!
The looming disruption of Generative AI
Now, the industry faces a disruption that is fast and far-reaching: Generative Artificial Intelligence. As The New York Times stated already in August 2023, "Publishing is facing a new disruption that is likely to be far more wide-ranging and transformative: the rise of artificial intelligence." (The New York Times).
Even Publisher’s Weekly, usually cautious about technology, described this shift as a "game changer—something fast, and transformative. Scary fast." (Publisher’s Weekly).
From the very creative process to manuscript acquisitions, editing, cover design, audiobook production, and marketing material development, AI is set to reshape nearly every aspect of book publishing. Some tasks will be automated, while others will be enhanced by AI, requiring professionals to upskill to stay relevant in this rapidly evolving landscape.
In the coming posts, we will delve deeper into how Generative AI is reshaping each aspect of the publishing process. Stay tuned for this exploration into the future of book publishing.
🛠️ Best gen AI tools to create music
⚠️ Note: this list of tools by AI Muse is not an invitation to purchase. Check the pricing and always read the terms and conditions.
Suno - Best for: Full song generation with vocals and background music.
Key Features: Suno is highly regarded for its ability to generate entire songs from text prompts, including vocals, instruments, and background music. It allows users to input a song description and style, producing complete tracks within seconds. Suno is praised for its high-quality audio output and ease of use.
Pricing: Free (50 credits/day), paid plans start at $8/month.
Why it stands out: Suno is considered one of the most reliable AI music generators due to its accuracy in adhering to prompts and producing professional-sounding tracks.
Udio - Best for: Generating songs with strong melodies.
Key Features: Udio excels at producing music with clear melodies and allows users to customize lyrics, genres, and instruments. It’s particularly useful for creating catchy tunes quickly and efficiently.
Pricing: Free during beta testing.
Why it stands out: Udio is known for its quality outputs, especially in genres like blues and hip-hop, making it a strong competitor to Suno.
AIVA - Best for: Composing cinematic and classical music.
Key Features: AIVA specializes in generating orchestral compositions across various genres like cinematic, electronic, and jazz. It offers deep customization options, including mood, genre, tempo, and instruments. AIVA also provides MIDI editing capabilities.
Pricing: Free plan (3 downloads/month), paid plans start at €15/month.
Why it stands out: AIVA is ideal for professionals looking to create complex compositions for film scoring or game development.
Soundraw - Best for: Customizable background music.
Key Features: Soundraw allows users to generate music based on mood, genre, and length while offering detailed control over tempo, key, and instrumentation. It’s perfect for content creators needing background tracks that fit specific moods or scenes.
Pricing: Free plan available; paid plans start at $16.99/month.
Why it stands out: Soundraw’s strength lies in its user-friendly interface and the ability to fine-tune tracks manually after AI generation.
Beatoven.ai - Best for: Custom beats for multimedia projects.
Key Features: Beatoven.ai focuses on generating royalty-free beats tailored to specific moods or genres. It allows users to adjust rhythm, tempo, and other elements in real-time.
Pricing: Free trial available; paid plans start at ₹299/month (~$4).
Why it stands out: Beatoven is ideal for creators looking for unique beats that can be used in podcasts, videos, or other media without worrying about copyright issues38.
Mubert - Best for: Real-time music generation for live streams or apps.
Key Features: Mubert offers real-time adaptive music generation tailored to specific contexts like live streams or mobile apps. It also provides an API for developers to integrate AI-generated music into their platforms.
Pricing: Free plan available; paid options depend on usage needs.
Why it stands out: Mubert’s ability to generate dynamic soundtracks makes it ideal for interactive projects.
Soundful – Best for: Quick production of royalty-free tracks.
Key Features: Soundful offers template-based music creation across multiple genres with fully mastered tracks ready for commercial use. It’s designed for non-musicians who need high-quality music fast.
Pricing: Free plan (10 downloads); premium plans start at $9.99/month.
Why it stands out: Soundful is great for content creators who need professional-grade tracks without the hassle of complex production processes.